
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <ctime>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
srand((unsigned int)time(NULL));
int succ1 = 0, succ2 = 0;
for (int t = 0; t < 1000000; t++)
{
int count1 = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++)
{
if (rand() % 6 == 0)
{
count1++;
break;
}
}
if (count1 > 0)
succ1++;
int count2 = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 12; i++)
{
if (rand() % 6 == 0)
count2++;
}
if (count2 > 1)
succ2++;
}
cout << succ1 / 1000000.0 << " " << succ2 / 1000000.0 << endl;
return 0;
}srand((unsigned int)time(NULL)); 난수 발생기의 시드를 설정합니다. 이를 통해 rand() 함수가 호출될 때마다 다른 시퀀스의 난수를 생성할 수 있습니다. 시드를 현재 시간으로 설정함으로써 더 무작위성을 높입니다.
int succ = 0, succ = 0; 성공 횟수를 저장하는 변수 succ1과 succ2를 초기화합니다.
for문을 통해 1000000만번 반복하는 루프를 생성하고 1회 이상 성공할 확률을 계산합니다. for(int i =0; i<6; i++)에서 6번의 시도를 반복하면서 rand % 6 == 0 을 통해 나머지가 0인지의 확률을 계산합니다. 만약 성공하면 count1를 증가시킵니다. count1이 0보다 크면 최소한의 한번 이상을 성공한 것이기에 succ1을 증가시킵니다.
두 번째 루프도 비슷한 방식으로 풀면 됩니다.

#include <iostream>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cmath>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int n, k;
cin >> n;
int integers[100];
double sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
cin >> integers[i];
sum += integers[i];
}
double SumofDifference = 0;
double avg = sum / n;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
SumofDifference += pow(integers[i] - avg, 2);
}
double standardDeviation = sqrt(SumofDifference / n);
cout << sum / (double)n << " " << standardDeviation << endl;
}
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cmath>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int n;
cin >> n;
int num[10] = {0,};
while (n > 0)
{
num[n % 10]++;
n /= 10;
}
for (int c : num)
cout << c << " ";
return 0;
}간단하게 풀 수 있는 문제입니다. while문을 사용하여 120341279라는 예시를 /10을 해주는 방식을 일의자리, 십의자리 ... n의 자리 까지 구해주는 방식입니다.
그리고 for문을 저런 식으로 걸어주면 간단하게 출력이 됩니다.

#include <iostream>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cmath>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int n, k;
cin >> n;
int array1[100];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
cin >> array1[i];
}
cin >> k;
int min = abs(array1[0]-k);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
if (abs(array1[i] - k) < min)
min = abs(array1[i] - k);
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
if (abs(array1[i] - k) == min)
cout << array1[i] << endl;
}
return 0;
}이것을 풀려면 abs의 사용법을 아셔야 합니다. abs()는 절댓값을 구해주는 함수입니다. <cmath> 를 include 해주어야 하며 이것만 안다면 for문과 if문을 잘 겹합하여 문제를 풀 수 있습니다.
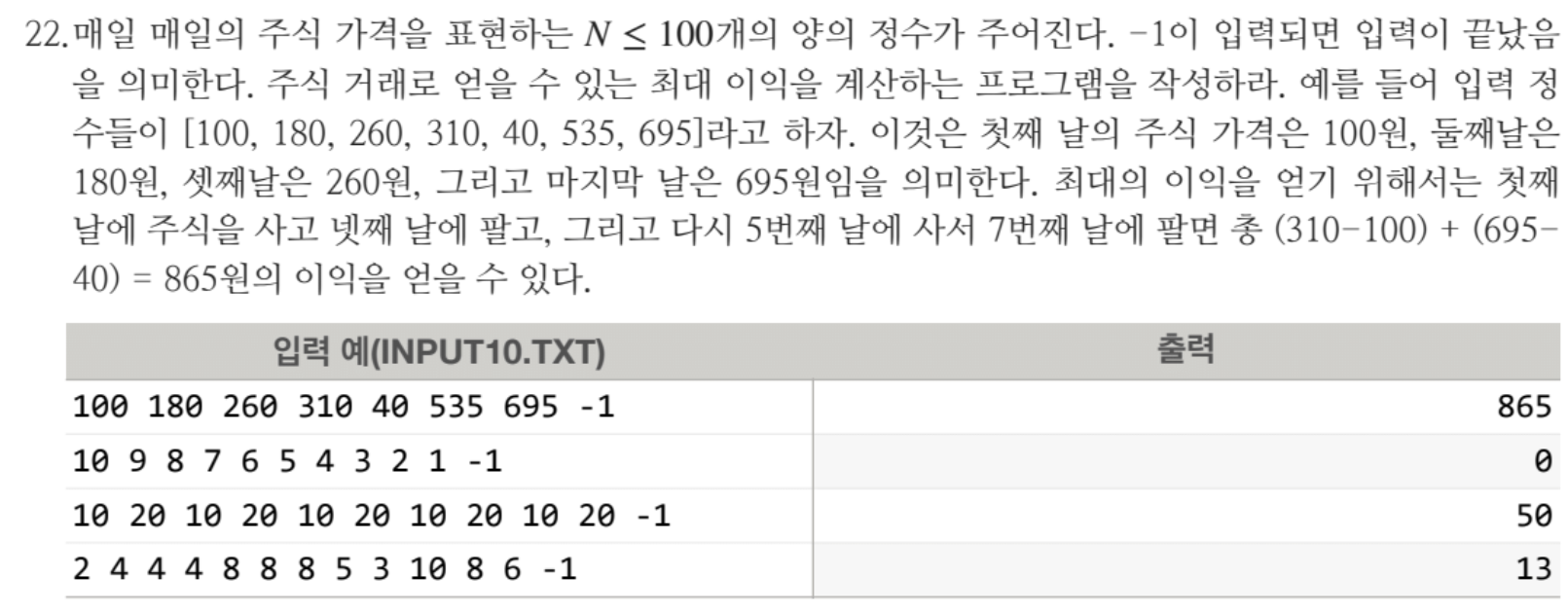
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cmath>
using namespace std;
const int MAX = 100;
int main()
{
int data[MAX], k, n = 0;
while (1)
{
cin >> k;
if (k == -1)
break;
data[n++] = k;
}
int gain = 0;
int total_gain = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++)
{
if (data[i] >= data[i - 1])
gain += (data[i] - data[i - 1]);
else
{
total_gain += gain;
gain = 0;
}
}
cout << total_gain + gain;
return 0;
}while(1)에선 if (k == -1) break; 를 통해 -1이 나온다면 break를 해주도록 되어 있습니다. 그리고 data[n++] = k를 통해서 data[0] 부터 data[n] 까지 정의되도록 나와있습니다. 후치수식을 해주기 때문에 data[0]도 들어가는 것입니다.
그 다음 int gain, total_gain을 정의를 해줍니다. 이것은 탐욕적 알고리즘을 쓴 것인데요. 각 단계에서 지금 가장 좋은 선택을 하고 이전 날짜보다 높으면 이익으로 취급하는 것입니다.
for(int i=1; i<n; i++)를 통해 data[1] data[0] 부터 각각 data[n-1] - data[n-2] .. 이렇게 비교를 통해 해줍니다. 만약 작다면 gain을 total_gain으로 넘겨준 후 다시 gain을 0부터 진행합니다.
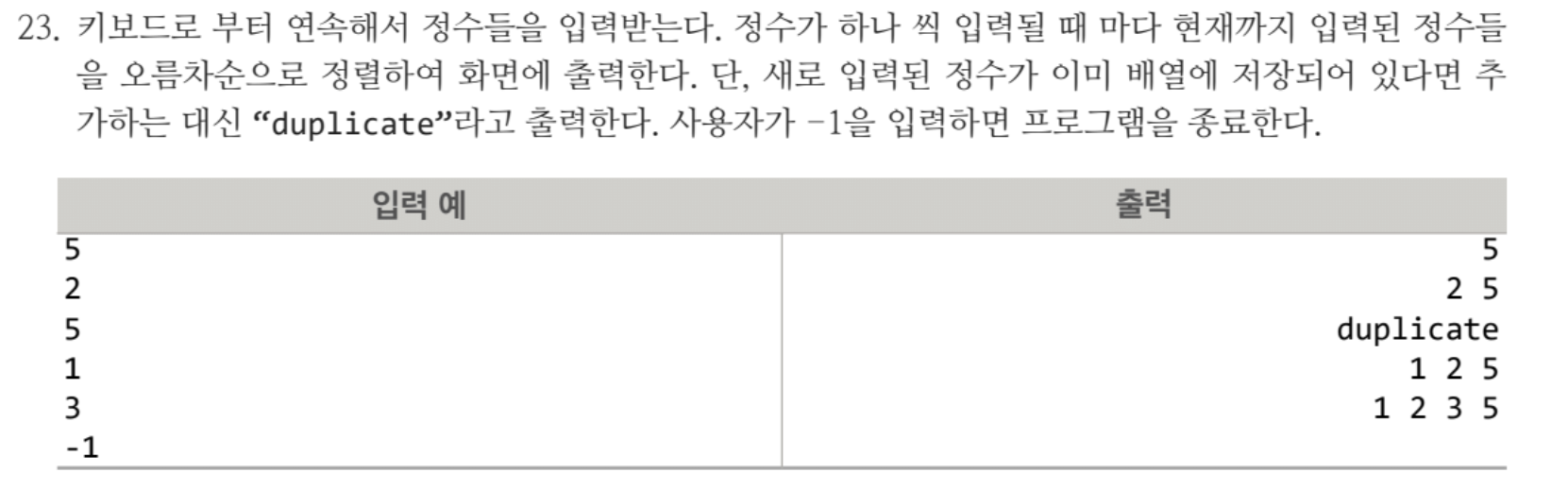
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cmath>
using namespace std;
const int MAX = 100;
int main()
{
int n = 0, t;
int data[MAX];
while (1) {
cin >> t;
if (t == -1) break;
// 중복을 확인하는 코드를 배열에 값을 저장한 후에 실행합니다.
bool duplicate = false;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
if (data[i] == t)
{
cout << "duplicate" << endl;
duplicate = true;
break;
}
}
if (duplicate)
continue;
// 중복이 아닌 경우에만 배열에 값을 저장합니다.
data[n] = t;
n++;
// 삽입 정렬을 사용하여 배열을 정렬함
int j = n - 1;
while (j > 0 && data[j - 1] > data[j])
{
swap(data[j], data[j - 1]);
j--;
}
// 정렬된 배열 출력
for (int k = 0; k < n; k++)
cout << data[k] << " ";
cout << endl;
}
return 0;
}int n = 0, t; int data[MAX] 변수 n은 현재까지 배열에 저장된 값의 개수는 나타내고 data[MAX]는 최대 크기인 MAX인 배열의 입력된 값을 저장합니다.
while(1)을 통해 무한루프를 시작하며 if (t == -1)이면 break;를 해줍니다.
이후 bool duplicate = false를 선언해줘서 만약 dupllicate가 나올 때는 continue;를 통해 처음으로 돌아가게끔 해줍니다. if (duplicate) continue;
data[n] = t; n++; 는 중복된 값이 없으면 배열에 t를 저장하고 배열의 크기를 1 증가시킵니다.
이후
int j = n-1에서 변수 j를 선언하고 배열의 마지막 인덱스를 초기화합니다. 또한 while(j>0 && data[j-1] >data[j]) {...} 을 통해 삽입 정렬 알고리즘으로 배열을 정렬합니다.

#include <iostream>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cmath>
using namespace std;
const int MAX = 100;
int main()
{
int n = 0;
int data[MAX];
cin >> n;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
cin >> data[i];
}
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++)
{
int maxIndex = i; // 현재까지의 최댓값의 인덱스
for (int j = i + 1; j < n; j++)
{
if (data[j] > data[maxIndex])
{
maxIndex = j; // 최댓값의 인덱스 업데이트
}
}
// 최댓값을 현재 위치로 이동
if (maxIndex != i)
{
swap(data[i], data[maxIndex]);
}
}
// 정렬된 배열 출력
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
cout << data[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}'IT 프로그래밍 > 객체지향프로그래밍' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 객체지향프로그래밍 1번, 2번, 3번, 4번, 5번, 6번 (0) | 2024.04.20 |
|---|---|
| 객체지향 프로그래밍 25번 , 26번, 28번, 29번, 30번, 31번, 32번, 33번 (0) | 2024.04.20 |
| 객체지향 프로그래밍 13번 , 14번, 15번 (0) | 2024.04.20 |
| [C++] 12번 (0) | 2024.04.17 |
| [C++]음이 아닌 정수 중 최소값 출력, 이진수 변환 출력 (0) | 2024.04.17 |